Life Cycles will be focusing on the life cycles of invertebrates, fish, birds, mammals, reptiles, amphibians, and plants. This program will include a lesson plan, activities, and stations of biofacts, information, and hands-on tactile components. This program will also include an English portion, learning about the stages of a story and creating a group skit about one of the life cycles they have been educated on to perform to their classmates.
There are 4 Life Cycle kits to choose from. These are listed below. If you have a preference please indicate when inquiring about a booking.
Life Cycles kits are:
- Life Cycles I - Invertebrates
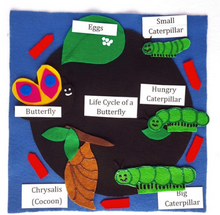
- Dragonfly, Butterfly, Lobster, Spider, Worms
- Life Cycles II - Vertebrates
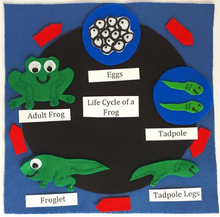
- Bat, Goose, Frog, Turtle, Shark
- Life Cycles III - Mixture A
- Wolf, Scorpion, Tree, Salamander, Butterfly
- Life Cycles IV - Mixture B
- Crab, Robin, Salmon, Bee, Bean/Flower
Life Cycles kits include:
- The rental is for your school
- As many teachers at your school may use this kit within the rented week(s) time
- A lesson plan (including topics on living and non-living, needs to survive, habitats, animal and plant life cycles, and elements of a story)
- Felt life cycle puzzles
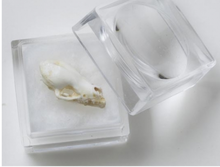
- Biofacts (real and replicated animal and plant pieces such as skulls etc)
- North America's First People's meanings and importance of a spider, wolf, salmon, and turtle.
- Additionally, it aligns with First Peoples Principals of Learning.
Cost to rent:
The rental cost for one week is $100
Plus:
Refundable deposit $200
Shipping $100+ (depending on where you are located)
Pick up and drop off within Calgary - Free
*Price is subject to change
Testimonials
How do you order a FIELD Kit?